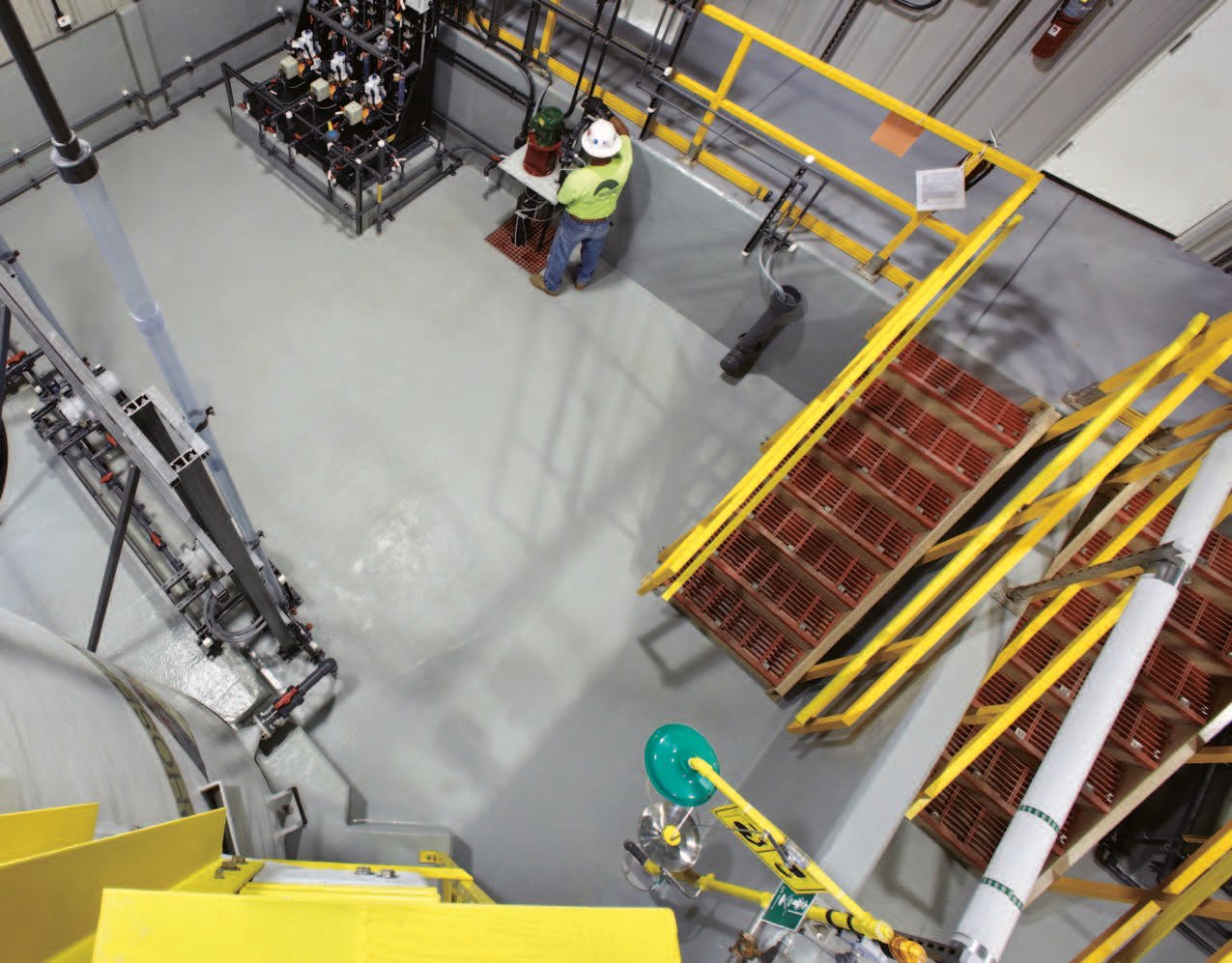

Exploring Secondary Containment linings
Dive deep into the world of secondary containment coatings, understanding their crucial role in industrial safety and environmental protection.
- Rick Gilbreath
Dive deep into the world of secondary containment linings, understanding their crucial role in industrial safety and environmental protection.
Understanding Secondary Containment Linings: An Overview
 Secondary containment coatings are specialized barriers designed to prevent hazardous substances from escaping into the environment in the event of a spill or leak from their primary containment vessels. These coatings are applied to containment systems, which are structures or spaces that hold potentially harmful chemicals or pollutants. The intended purpose of secondary containment coatings is to provide a durable, impervious surface that can withstand aggressive chemicals and environmental conditions.
Secondary containment coatings are specialized barriers designed to prevent hazardous substances from escaping into the environment in the event of a spill or leak from their primary containment vessels. These coatings are applied to containment systems, which are structures or spaces that hold potentially harmful chemicals or pollutants. The intended purpose of secondary containment coatings is to provide a durable, impervious surface that can withstand aggressive chemicals and environmental conditions.
The importance of secondary containment coatings cannot be overstated. They are critical components in managing risks associated with the storage and handling of hazardous materials. By ensuring that these coatings are properly specified and applied, industries can protect the environment, comply with regulations, and minimize the potential for costly cleanups and fines.
Comparing Chemical Resistant Floors and Secondary Containment Coatings
While chemical resistant floor coatings and secondary containment coatings both serve to protect against hazardous substances, their applications and characteristics differ. Chemical resistant floor coatings are designed to resist corrosion, wear, and degradation from frequent or occasional chemical exposure, typically where the chemical will be cleaned up in a timely manner. These systems are commonly used in areas where chemicals are handled regularly. These floor coatings are integral to the safety of day-to-day operations.
Secondary containment coatings, on the other hand, are specifically engineered to contain spills or leaks from primary containment units, such as tanks or drums. The design of these systems should be designed to contain the entire contents of the primary containment vessels, along with an additional volume of liquid to account for potential rainfall or groundwater runoff, without allowing a breach of the lining for a minimum of seventy-two (72) hours. They are an additional safety measure, providing a second line of defense. These coating systems are often more robust and have to adhere to stricter regulatory standards to ensure that they can contain substances for extended periods without failure.
The Role of Fiberglass Reinforcement in Secondary Containment Systems
Fiberglass reinforcement is commonly utilized in secondary containment systems to enhance the structural integrity and chemical resistance of the coatings. Adding fiberglass increases the strength, reducing the likelihood of cracking and damage over time. It also ensures that the containment system can endure the mechanical stresses
that may arise during a spill event.
Although not always required, fiberglass reinforcement is often regarded as best practice in numerous situations, particularly where there is a high risk of exposure to aggressive chemicals. The choice to incorporate fiberglass reinforcement should be guided by a risk assessment of the stored materials, the potential impact of containment failure, and the specific guidelines set by regulatory authorities.
Navigating Regulatory Standards and Enforcement Agencies
Secondary containment lining systems must comply with regulations at the local, state, and federal levels. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is the main authority enforcing rules related to spills and cleanup operations. The EPA's Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) regulations establish requirements for secondary containment to prevent oil spills from contaminating navigable waters or nearby shorelines.
 Asset owners must adhere to these regulations to avoid fines and ensure their activities do not harm the environment. It is crucial for organizations to stay updated on relevant regulations and standards, such as those from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the American Petroleum Institute (API), to maintain compliance and protect their operations.
Asset owners must adhere to these regulations to avoid fines and ensure their activities do not harm the environment. It is crucial for organizations to stay updated on relevant regulations and standards, such as those from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the American Petroleum Institute (API), to maintain compliance and protect their operations.
Best Practices for Choosing and Applying Secondary Containment Coatings
Choosing the appropriate secondary containment coating is a crucial decision influenced by several factors, such as the type of chemicals stored, the site's environmental conditions, and the physical attributes of the containment area. Consulting with coating manufacturers and specialists is essential to identify the most suitable product for the specific application.
Ensuring the proper application is crucial for the containment system's effectiveness. This includes preparing the surface, applying the coating as per the manufacturer's guidelines, and allowing sufficient curing time. Regular inspections and maintenance are also essential to maintain the coating's integrity and performance. Adhering to these best practices helps businesses ensure their secondary containment systems are dependable and meet regulatory standards.
Check out these additional resources
Secondary Containment Coatings- What you need to know
What Coatings Should Be Used for Secondary Containment?
Don't miss these project profiles
Town of Gilbert NWTP Containment

NSF-Approved Coatings for Potable Water Tanks
Safe and Clean drinking water is crucial, but how...
Tnemec Aerolon vs. Competitors: Which Safety...
Explore the revolutionary properties of Tnemec...

How Our Coatings Ensure Compliance for Potable...
Public Health is more important than ever, when...
_Page_1_Image_0001.jpg?width=328&height=251&name=APP%20GUIDE_Series%20237SC-280%20(MCK)_Page_1_Image_0001.jpg)